About
OpenDNSSEC was created as an open-source turn-key solution for DNSSEC. It secures zone data just before it is published in an authoritative name server.
Why DNSSEC?
Many internet protocol hinge on DNS, but the data in DNS caches has become so vulnerable to attack that it cannot be relied upon anymore. The added authenticity in DNSSEC makes sure that such attacks have no effect.
That is, if
- Zones are verified. Easy-to-deploy software for DNSSEC-aware name resolving (and caching) exists, for example Unbound or properly configured Bind9.
- Zones are secured. Easy-to-deploy solutions for DNSSEC did not yet exist, at least not in open source. Hence the OpenDNSSEC project.
More on the problems with DNS and about deploying DNSSEC can be found in this white paper.
Note:
At present, the relationship between a secure zone and its parent cannot be automatic, in lieu of standards. This means that you will be required to communicate with your parent zone registrar about once a year, with any DNSSEC product.
What does OpenDNSSEC do?
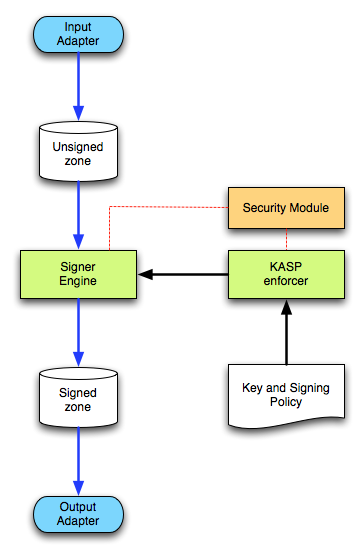
OpenDNSSEC takes in unsigned zones, adds the signatures and other records for DNSSEC and passes it on to the authoritative name servers for that zone.
DNS is complicated, and so is digital signing; their combination in DNSSEC is of course complex as well. The idea of OpenDNSSEC is to handle such difficulties, to relieve the administrator of them after a one-time effort for setting it up.
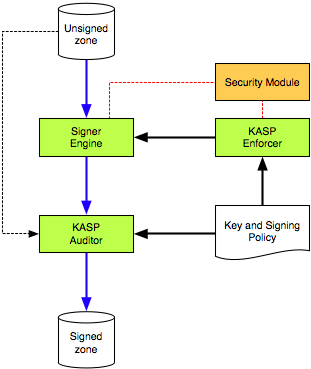
Architecture overview for 1.3
Key Storage (HSM)
All keys are stored in a Security Module and accessed via PKCS#11, a standard API (software interface) for communicating with devices which hold cryptographic information and perform cryptographic functions. To deploy OpenDNSSEC, an implementation of this API is required, e.g. a software implementation like softHSM or a hardware device like an HSM or a smartcard/token. Whether you should use a “soft” or “hard” implementation (or a combination thereof) depends on your security requirements. Some guidance can be found in the HSM Buyer’s Guide. A list of tested implementations can be found in the list of HSM vendors.